Climate Change
What is climate change?
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions, or in the distribution of weather around the average conditions (i.e., more or fewer extreme weather events).
Climate change is caused by factors that include oceanic processes (such as oceanic circulation), variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics and volcanic eruptions, and human-induced alterations of the natural world; these latter effects are currently causing global warming, and "climate change" is often used to describe human-specific impacts.
Global Warming
What is Global Warming?
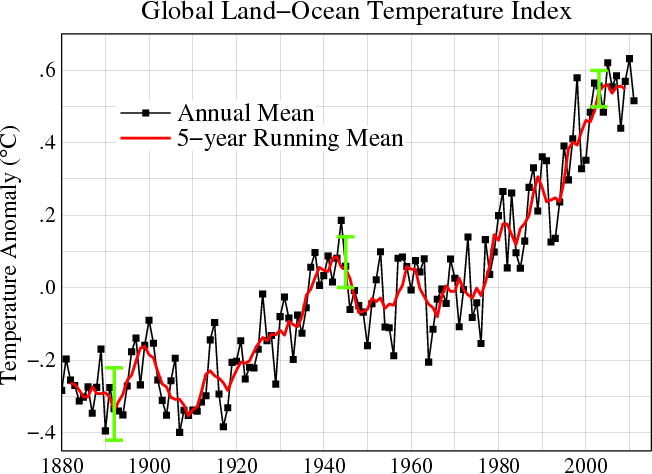
Global warming is the rise in the average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans since the late 19th century and its projected continuation. Since the early 20th century, Earth's mean surface temperature has increased by about 0.8 °C (1.4 °F), with about two-thirds of the increase occurring since 1980.
Warming of the climate system is unequivocal, and scientists are more than 90% certain that it is primarily caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases produced by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. These findings are recognized by the national science academies of all major industrialized nations.
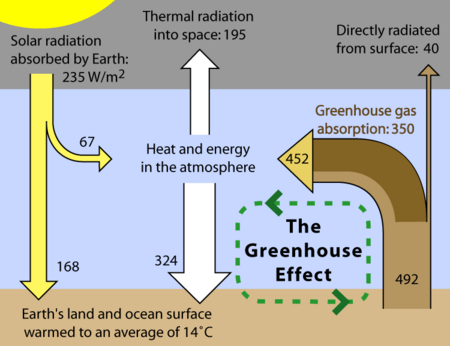
The Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is re-radiated in all directions. Since part of this re-radiation is back towards the surface and the lower atmosphere, it results in an elevation of the average surface temperature above what it would be in the absence of the gases.
The impact of climate change on coastal Australian waters
Climate change will impact on several areas of importance in the Australian coastal regions. The Australia government have published a report on the risks of climate change. The report presents the findings of the first pass national assessment of the risks of climate change for the whole of Australia's coast.
How climate change will impact on the marine environment are summarized below:
Increased Water Temperature
Southward migration of tropical and temperate species. Increased frequency of coral bleaching episodes. Declining kelp forests off eastern Tasmania (Edyvane 2003; Edgar et al. 2005).
Ocean chemistry (acidity)
Increased CO2 absorption by the ocean decreases pH of the ocean and reduces availability of calcium carbonate which may impair the survival of organisms with calcium carbonate shells.
Ocean Circulation and Overturning
Changes to larval transport and upwelling regions and subsequent changes to productivity.
Increased Oceanic Sratification
Reduced overturning and nutrient cycling
Cloud Cover and Solar Radiance
Changes in the light supply to the ocean surface with influence on productivity. Increased storminess Increased turbidity, destruction of marine habitat such as coral reefs during extreme events.
Sea Level Rise
Potential loss of mangrove forests and nursery grounds for marine species.
Resources:
Climate Change the risks to Australias coast, on-line at:http://www.climatechange.gov.au/~/media/publications/coastline/cc-risks-full-report.pdf
What is climate change? modified from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Climate_change, licenced under Wikicommons, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License (“CC BY-SA”).
What is Glodal Warming? modified from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_warming , licenced under Wikicommons, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License (“CC BY-SA”).
Greenhouse Effect modified from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greenhouse_effect , licenced under Wikicommons, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License (“CC BY-SA”).

 Marine Science Australia
Marine Science Australia